Do you really know what cigarettes are made up of?
Do cigarettes are really consumable or we are just paying hefty taxes to the Government. What do you think who is maximising the returns? For this just check it out this article.
Cigarette consumption has become a new cool thing, it projects something rich, premium or a status quo for some people. What does cigarette really constitute?
So let’s take a deep dive on how the cigarettes are made, Taxation and Business Margins and some fun facts. So let’s start with the production.
Production of Tobacco.
During the year 2018-19, the tobacco board marketed a quantity of 222.49 million kg in its auction platforms in both Andhra Pradesh and Karnataka at an average price of ` 134.45 per kg as against 205.94 million kg marketed at an average price of 137.07 per kg during the year 2017-18. 2,20,517 Metric tons of tobacco and tobacco products were exported from India during 2018-19 valued at 6,001.02 crores and have increased by 4% in quantity terms and 8% in Value terms respectively when compared to last year. However, in dollar terms, the value of exports is 858.52 million US$ and have declined by 0.11% on year to year basis. - fact sheet by Tobacco Board.
Process
The process of making cigarettes begins in the field where the tobacco is grown and harvested. India is the Third-largest exporter of tobacco. Andhra Pradesh and Karnataka hold more than 80% of the market in producing tobacco.
During 2018-19 Tobacco Board had increased the crop size for the cultivation of FCV ( (Explained this term later on) tobacco to 236 million kg from 235 million kg fixed during 2017-18 crop season.
There are mainly two types of domestic tobacco, bright (which is also called flue-cured Virginia (FCV)) and burly. The unique taste of cigarettes is a result of the blending of Burley and FCV tobacco's, The process of harvesting and Cultivating is known as curing.
Tobacco leaves are shipped to a warehouse where stems and veins are separated from the lamina, the lamina is the preferred part of the tobacco leaf. The lamina is sent to a storehouse where it is kept for tobacco to dry and aged for 2 months to two years to mellow and develop its flavor during the ageing process. ( Similar process like Wine and Whiskey).
There are five other components of the tobacco blend:
1.Reconstituted,
2. Blended leaf,
3. Improved stem
4. Expanded stem and
5. Expanded tobacco.
Let's look at each of those five components. Reconstituted leaf( RL) is comprised of stems, small lamina and other small particles of tobacco recovered from the manufacturing processes. In order to be utilized in cigarette manufacturing, RL is processed into a form to resemble lamina much like a sheet of paper.
In order to make that RL sheet, the water-soluble material must be separated from the tobacco fibre. This is done by adding hot water and agitating. It to separate the water-soluble material from the tobacco fibre once the liquid is separated from the tobacco fibre. The fibre is refined and processed into sheet form. The separated water-soluble material contains numerous compounds, all of which existed in and were naturally extracted the tobacco material. The water is partially evaporated, leaving the tobacco solubles. The solubles are then mixed with flavourings, preservatives and humectants, which help maintain moisture and pliability.
The tobacco solubles are then reapplied to the RL sheet. The RL is dried cut into lamina sized pieces and is ready to become part of the tobacco blend. At no point in the RL reconstituted leaf process is additional nicotine introduced. In fact, the nicotine level in the finished RL is 20 to 25 % lower than the nicotine level in the raw materials.
Blended Leaf (BL) is comprised of Burley stems and small tobacco particles recovered from tobacco processing. They are ground to a uniform size, blended and mixed with processing Chemicals to release the pectin (a naturally occurring carbohydrate in plants when heated pectin forms a gel-like material that binds the particles together). Flavourings, humectants and preservatives are added and the mixture is cast onto a moving belt, heated and dried to form the sheet. It is further dried and cut into lamina sized pieces, and then it too is ready to become part of the tobacco blend.
The last three components are Improved Stem (IS), Expanded Stem(ES) and Expanded Tobacco (ET). Tobacco is all made from tobacco components that have been expanded or puffed up the use of expanded products make cigarettes more cost-effective to produce because expanded tobacco has increased volume and lower weight.
IS and ES are made from bright(FCV). Tobacco stems which yield less tar and nicotine than lamina expanded products are manufactured with two basic processes, IS and ES used bright tobacco stems that are moistened with water and steam. The stems are, then rolled and cut. Humectants are added. As for moisture retention, sugar is added for flavour, the ES is dried in an expansion Tower to its final moisture.
Improved Stem(IS) made by steaming and then drying to produce expansion Expanded Tobacco (ET) uses, cut bright and burly lamina with sugar and humectants added, and then it is impregnated With liquid carbon dioxide and expanded in a tower much the same as ES at this point, Expanded Stem (ES) and Expanded Tobacco( ET) are complete and ready to be blended, with the Burley lamina, bright lamina. Never at any point in the processing of any of these components has any additional nicotine being introduced.
The components are then transported to the cigarette manufacturing facilities, depending on which brand of cigarette is to be produced. The amount of each component to be used is selected by computer based on leaf Department formulation, the bright and burly lamina and oriental ( one type of tobacco) tobacco's are individually conditioned with steam to increase, moisture and temperature to reduce breakage. The leaf separation process is continued in the feeders and air separators.
According to the formulations for each cigarette brand, that partial blend is steamed and then goes to the cutting line where it is cut to a uniform size and sent to a rotary dryer to reduce and control the moisture content at this point, the small lamina is added in brand-specific formulations and the total blend. All the tobacco that goes into a cigarette is now complete. The tobacco then goes to the flavour cylinder where final flavourings are added using denatured. There is less nicotine in the final tobacco blend and indeed the final cigarette then existed in the tobacco materials before they were harvested or processed. Once the final flavourings are added to the tobacco, it is put in short-term storage. The total blend is then fed into cigarette making machines where it is rolled in paper and a long continuous cigarette rod is created. It is then cut to a specific length, depending on the brand and delivered to the tipping machine where the filter is applied. The finished cigarettes are then packaged, sealed and ready for shipment.
Before we move ahead, If you still left to subscribe Equitymaniac, Please do
Taxation and Margins.
The cigarette is a highly taxable product over the world. In India, Cigars and Cigarillos will be charged at the rate of 28% (GST) and an additional cess up to 21% or Rs 4.170 per stick would be levied.
Chewing tobacco has also been kept under the 28% category and an additional cess of 142% would be levied upon chewing tobacco (with lime tube) and 160% on chewing tobacco (without lime tube). (You can check from the image given below, what taxes do these cigarettes companies pay to the government.)
Let’s take a hypothetical example
Mr A is a cigarette manufacturer and producing 72 mm cigarettes for their end consumer, Mr A has a cost of 2 rs/ cigarette after procuring tobacco, processing and branding.
How much MR. A tax will be paid to Government?
As you know the cost of making one cigarette is 2 rs while on that 2rs 28% of GST been levied that makes 2.56 and additional 5%+2.876 Per cigarette. So the total cost including taxes goes up to 5.564 Rs per cigarette i.e ~2.7X taxes are been levied on the cost.
Margins for the business is as follows
Flowchart
Manufacturer
The manufacturer has a high volume, high margin. In cigarettes, you can expect 10-25% of the net profit margin in the business. 12.5 grams of tobacco is filled in a 20 pack box which is equivalent to 0.7-1 gram of tobacco is filled up in one cigarette.
Cost of raw materials is very negligible. Processing, filling and preparing ( Finishing) a cigarette is the core cost of the manufacturer.
Regional Distributor
Regional Distributor is also called C&F ( In business terms). They have a low margin, high volume business. Regional distributor place direct order to the manufacturer. They have an advance payment or cash on the delivery system. They have a margin of 1.5%-2% on Sales. Due to the high volume business, they make an ample amount of money. The Regional distributor also earns a good amount of money by selling illegal cigarettes, as they don’t pay hefty taxes to the government.
Let me state a few unpopular facts
Only 9% of tobacco consumed in India constitute legal cigarettes, while 91% are from traditional products and illegal cigarettes.
This 9% contributes to 80% of the taxes collected by the Government of India from the tobacco sector.
High levels of taxation relative to other tobacco products and stringent regulations have also led to the rise in the illicit cigarette trade and consequent loss of revenue to the government.
Around 68% of tobacco consumption comes from the unorganised sector which bypasses the purview of the regulatory authorities and do not pay taxes.
It is estimated that on account of illegal cigarettes alone, revenue loss to the Government is almost 15,000 crores per annum.
India is currently the 4th largest illegal cigarette market in the world with illegal cigarettes reaching 26.5 billion sticks in 2018 which is double the level it was in 2005- Company Annual Report
District Distributor & Wholesaler
This segment also has a low margin high turnover business. Some companies pay a 1-1.5% commission on a sales basis. In this segment, you have to bear a cost of warehouse, salesman, delivery boy, administrator and a small office if you totalled up this cost you make just 0.5-0.7% of the total turnover. These margins are also fancy because they have a daily collection system or cash on delivery basis, so there is a very low chance of bad debt and their asset turnover increase significantly.
Retailer ( Pan Shop)
The retailer has a low volume high margin business.
Let’s take one example
Can you recall a brand called four square?. This product has an MRP of 85Rs (Pack of 10 Cigarettes). Retailer buys at 72-74Rs and sells a piece of cigarettes at 10Rs each which equivalent to 100rs per pack of cigarettes. You can calculate how much a retailer is earning.
So one question pops up in your mind?
Why retailer charges More price than MRP.
IF you notice in India, cigarette smoking is a sin, Even though you are an adult you are ashamed of smoking cigarettes in front of your loving ones, Cigarette culture is not so open in India. So every individual who is a smoker takes one or two cigarettes a day and don’t care about what price they charge, Many of even didn’t notice this fact. So this perspective takes us to behavior pattern of consumer. ( Just think and let me know about your answers).
Companies which are famous for making cigarettes and sales as of 2019 ( In US Billion $)
British American tobacco-33
Philip Morris International-30.2
Imperial Brands-20.5
Altria Group-20.5
Japan Tobacco-20
Gudang Garam-7.9
ITC-5.5
KT&G-4.3
ITC and Godfrey Philips are the major Cigarettes producer in India. Let’s check what brands they establish
Godfrey Philips has an established brand like Malboro ( Agreement with Philip Morris), Four Square, Red& White, etc and for the international market, they are present with the brand name called Blackjack, Cavandars, Stellars Etc.
ITC has an established brand like insignia, India Kings, Classic, Gold Flake, American Club, Navy Cut, Players, Scissors, Capstan, Berkeley, Bristol, Flake, Silk Cut, Duke & Royal.
Let see some facts about the Cigarette Industry and Consumption pattern of India.
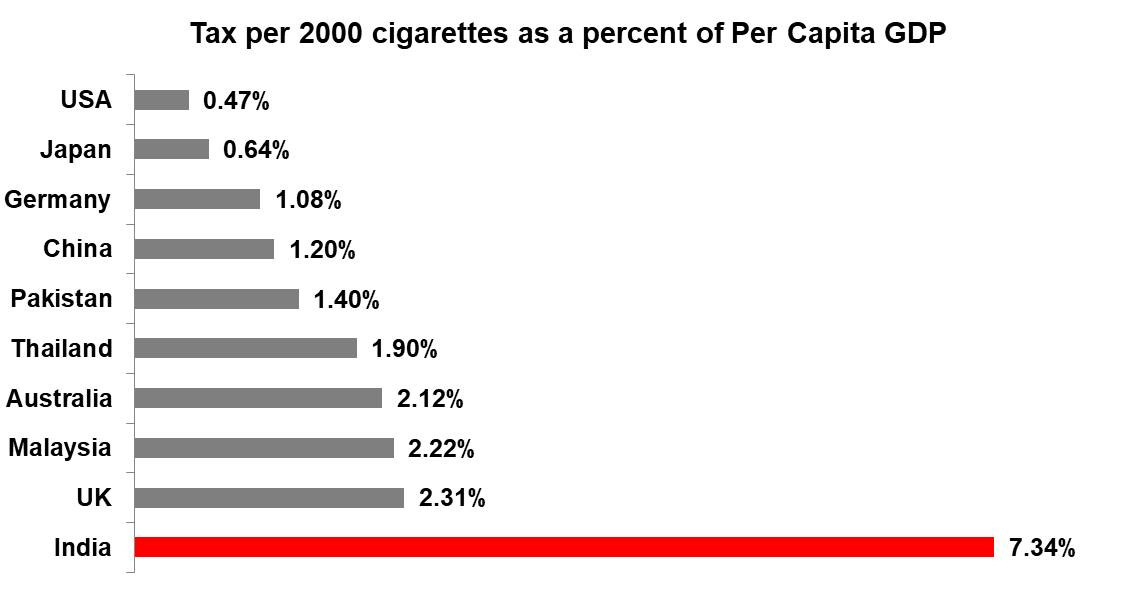
India has the highest tax on cigarettes as a % of capita GDP.
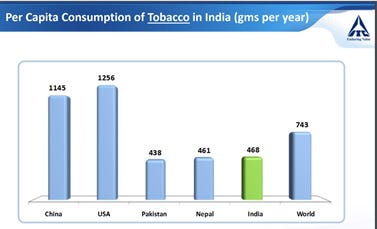
Per capita consumption is too low in India but these will be increasing in the near trend. ( Per capita = Applied to each person)
In rural areas, tobacco has more consumption compare to cigarettes, while we are the 3rd largest consumer of tobacco after China and USA
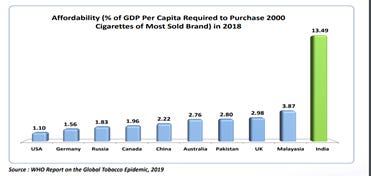
India ranks 1st in the most affordable for the consumption of Cigarettes.
Conclusion
I think after reading this piece you at least understand how this Industry/business works and some unpopular facts. Cigarette business is a cash business and has good potential in a near future. “ Smoking is a new Cool”- This tag endeavours youth on focusing in these areas. the consumer is very sticky when it comes to luxury products like Cigarettes, alcohol, etc. So I think for this sector there is vast potential and investing in this type of business can help us to generate a good amount of return of our capital.
If you are amazed by this article, please subscribe to equitymaniac for many such articles. ( I am Initiating with a new cool thing, so stay tuned)
Thanks For Reading,
Equitymaniac
Happy Investing.
(P.S- Conclusion is just an opinion and not a fact. please do your own due diligence before investing in any companies stated above. I am invested in some companies and willing to do so for a long term basis.)
Sources